When working with Ethernet networks—whether you're setting up a home router or managing enterprise infrastructure—you’ve likely encountered the RJ45 connector. It's the small, plastic plug at the end of your Ethernet cable, yet it plays a vital role in ensuring stable and high-speed communication between devices. But have you ever wondered how it actually works, how many pins it has, or why those pins matter?
In this article, we’ll break down everything you need to know about RJ45 connectors—from their internal pin configuration to wiring standards, cable categories, and their role in both data and power transmission.
How Many Pins Does an RJ45 Connector Have
What Is an RJ45 Connector ?
What Is the Most Common RJ45 Pinout ?
-Understanding T568A and T568B Standards
-T568B Pin Configuration Breakdown
-Straight-through vs. Crossover Cable Explained
Are Cat6 and Cat7 RJ45 Jack Connectors the Same ?
-Connector Format and Cross-Generation Compatibility
-Electrical Design and Shielding Capabilities
-Cross-Category Functionality and Use Cases
Why Do the 8 Pins in an RJ45 Jack Connector Matter ?
-Role in Data Transmission
-Integration with Power over Ethernet (PoE)
In the world of Ethernet cabling and networking devices, a common question is: How many pins are inside an RJ45 connector? The answer is straightforward—it contains 8 pins aligned in a single row within the transparent plastic housing. Each pin corresponds to one of the eight individual conductors in a standard Ethernet cable, forming the essential contact points for transmitting and receiving data. This 8-pin configuration supports high-speed communication across various networks, including LANs and WANs.
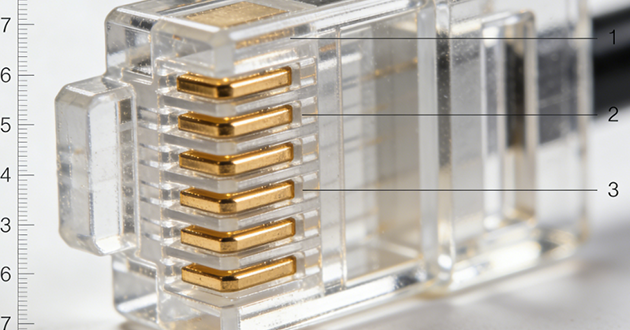
An RJ45 connector, short for Registered Jack 45, is a widely recognized modular plug used primarily for Ethernet-based networking. It provides the physical endpoint where twisted-pair Ethernet cables connect to network-enabled devices, including computers, switches, routers, and patch panels.
This type of connector follows the 8P8C standard, meaning it features 8 positions in its housing and 8 corresponding contacts that form electrical connections with the internal wires of the cable. Each of these eight metal contacts matches a specific wire inside the Ethernet cable, allowing for simultaneous data transmission across multiple channels.
RJ45 connectors are standard across several Ethernet cable categories, including Cat5, Cat5e, Cat6, and Cat7, making them a universal solution in both residential and enterprise networking environments.
Although similar in appearance to RJ11 connectors used for telephone lines, RJ45 plugs are not compatible with RJ11 jacks. The confusion between the two can lead to improper connections and even hardware damage. Below is a comparison to help differentiate them:
|
Feature |
RJ45 |
RJ11 |
|
Feature RJ45 RJ11 Pins |
8 |
4 or 6 |
|
Use Case |
Ethernet networking |
Telephone wiring |
|
Size |
Larger |
Smaller |
|
Compatibility |
Not interchangeable |
Not interchangeable |
Recognizing the difference between RJ45 and RJ11 is crucial when working with network infrastructure. Using the wrong connector type may result in poor connectivity or device malfunction, so proper identification is key to successful cable management and installation.
Want to explore more about how RJ45 connectors work and where they're used? Check out our in-depth guide: What Is an RJ45 Connector?
https://www.glgnet.biz/articledetail/what-is-an-rj45-connector-2025-guide.html

Properly wiring an RJ45 jack connector requires selecting the right pinout configuration, which determines how each internal wire in the Ethernet cable aligns with the connector's 8 pins. The two main standards you’ll encounter are T568A and T568B.
The T568A wiring scheme is often specified for residential applications and government projects. On the other hand, T568B is more prevalent in business and commercial networks, especially in North America.
Both schemes define how the eight color-coded conductors inside the cable are arranged in the connector. Although the color patterns differ, the performance is identical—as long as both cable ends follow the same layout. Mixing standards on either end creates a crossover cable, which may not work in all setups.
Here's how the wires are positioned using the T568B format, which is considered the default for most Ethernet cables:
|
Pin |
Wire Color |
Signal Role |
|
1 |
White/Orange |
Transmit + (TX+) |
|
2 |
Orange |
Transmit − (TX−) |
|
3 |
White/Green |
Receive + (RX+) |
|
4 |
Blue |
Unused for 10/100 Mbps |
|
5 |
White/Blue |
Unused |
|
6 |
Green |
Receive − (RX−) |
|
7 |
White/Brown |
Unused |
|
8 |
Brown |
Unused |
Note: In Gigabit Ethernet (1000BASE-T) networks, all eight wires are actively engaged in data transmission, utilizing all four twisted pairs.

A straight-through cable features identical pinouts on both ends (commonly T568B to T568B) and is ideal for connecting devices of different types—such as a computer to a network switch or router.
A crossover cable uses T568A on one end and T568B on the other. This configuration is primarily used to link similar devices directly, like PC to PC or switch to switch, without needing an intermediary device.
Tip: Most modern switches and routers include auto-MDIX, which automatically detects and adjusts for the cable type—making crossover cables less necessary in newer networks. Still, knowing the pinout structure remains important for manual installations or troubleshooting older equipment.
While Cat6 and Cat7 Ethernet cables may appear similar at first glance—often featuring identical RJ45-style connectors—their underlying specifications, intended performance, and compatibility considerations reveal several important distinctions.
Most Cat6 cables are equipped with standard RJ45 (8P8C) terminations, making them directly compatible with the vast majority of consumer and commercial network hardware. This connector type has become the de facto interface across modern Ethernet environments.
In contrast, Cat7 cabling was initially designed to utilize more advanced connection systems, such as GG45 and TERA, both developed to support superior shielding and higher operating frequencies. These connector types go beyond the limits of traditional RJ45, but are not as commonly adopted due to their limited backward compatibility.
To ensure widespread usability, however, many Cat7 cables are manufactured with RJ45-compatible connectors. This adaptation allows them to work within existing RJ45 infrastructure, even though the full capabilities of the Cat7 specification (e.g., up to 1000 MHz) may not be fully realized on standard ports.
The takeaway: RJ45 connectors are physically interchangeable across Cat5e, Cat6, and Cat7 cables, though the cabling and shielding behind them may differ significantly.

Cat6 cables generally rely on UTP (Unshielded Twisted Pair) construction, which is adequate for most environments with low to moderate electromagnetic interference. While STP (shielded) versions exist, they're less common in standard installations. Cat6 supports speeds of up to 10 Gbps, but optimal performance is typically limited to distances under 55 meters.
Cat7, by design, is built with individual shielding on each twisted pair, as well as an overall outer shield. This configuration—typically S/FTP or STP—is engineered to drastically reduce crosstalk and external EMI, making Cat7 ideal for noisy electrical environments or high-performance data infrastructure. It supports frequencies of up to 600 MHz, providing improved stability for demanding applications.
When terminated with RJ45 ends, Cat7 cables can be used with any device or port designed for Cat5e or Cat6. This backward compatibility ensures smooth integration into most existing networks.
However, it’s important to remember that the performance of the entire connection is only as strong as its weakest link. If you connect a high-spec Cat7 cable to a Cat5e switch, the data transfer speed and bandwidth will default to Cat5e limitations. This doesn’t reduce functionality, but it does limit throughput.
At the core of every Ethernet cable are eight individual conductors, arranged into four twisted pairs. These eight wires are directly mapped to the eight pins inside an RJ45 jack connector, and they play a crucial role in how data and—at times—power are transmitted across a network.
Each twisted pair carries electrical signals used for communication between devices. The number of active pairs—and therefore pins—depends on the Ethernet standard in use:
Fast Ethernet (10/100 Mbps): Utilizes only two pairs (4 pins). One pair handles data transmission while the other manages data reception.
Gigabit Ethernet (1000BASE-T): Engages all four pairs (8 pins) simultaneously. This enables full-duplex communication, where data flows in both directions over every pair at the same time, significantly increasing throughput.

Beyond just data, the 8-pin design also enables Ethernet cables to deliver electrical power alongside network signals through Power over Ethernet (PoE) technology.
Depending on the PoE standard (such as IEEE 802.3af, 802.3at, or 802.3bt), power can be transmitted in different ways:
Mode A: Power runs over the same pairs used for data (pins 1, 2, 3, and 6).
Mode B: Power is sent through the unused pins (4, 5, 7, and 8) in 10/100 Mbps networks.
4-pair PoE (e.g., PoE++): Delivers power over all 8 pins, providing up to 90W—ideal for high-power devices like PTZ cameras or wireless access points.
Whether you're building a simple LAN or powering smart devices through PoE, the full 8-pin configuration of an RJ45 jack connector is essential for supporting today’s high-speed and multifunctional Ethernet technologies. It’s not just about data—these pins carry the backbone of modern digital infrastructure.
Read more
https://www.glgnet.biz/articledetail/how-to-connect-an-rj45-connector.html
https://www.glgnet.biz/articledetail/what-are-rj45-connectors-used-for.html
Conclusion
Understanding the RJ45 connector goes beyond just knowing it has 8 pins—it’s about recognizing how those pins enable fast data transfer, power delivery, and broad compatibility across cable types like Cat5e, Cat6, and Cat7.