modern networking, SFP ports (Small Form-factor Pluggable ports) play a critical role by enabling flexible connectivity using either fiber optic or copper connections. Whether you're managing a data center, building a business network, or maintaining industrial infrastructure, a malfunctioning SFP port can cause significant disruptions.
In this article, we’ll break down the most common causes of SFP port failures—and the practical fixes for each. We’ll also share how GLGNET’s standards-based SFP cages and connectors, with configurable EMI/thermal/front-panel options, can help make deployments more stable and service-friendly.
An SFP port is a modular interface found on switches, routers, media converters, and other networking equipment. It allows you to plug in a compatible SFP transceiver (fiber or copper) to connect different types of network media.
Depending on the module, SFP ports support speeds from 100 Mbps up to 10 Gbps (with SFP+) and even higher with QSFP variants. Due to their flexibility and compact size, SFP ports are widely used in enterprise networks, data centers, FTTH, and industrial Ethernet applications.
To make that flexibility work in a real chassis, the SFP cage and connector behind the port are just as important as the transceiver—especially when you’re dealing with tight SFP port spacing, EMI at the front-panel opening, and day-to-day maintenance. GLGNET provides SFP cage and connector solutions in single- and multiport designs, with optional EMI gaskets or spring fingers, as well as light pipes and heatsinks to support dense layouts and higher-power modules.
Let’s break down the most frequent causes of SFP port issues and how to fix them.
A common reason your SFP port might not be working is that the SFP module you're using is simply not compatible with your device. Many major brands, including Cisco, HP, and Juniper, use strict module authentication protocols to restrict unsupported or third-party transceivers.
Example case:
An IT manager in California noticed immediate uplink instability after inserting a third-party 1G SFP into a Cisco Catalyst 9200. The interface would either stay down or flap repeatedly, and the switch would log an “Invalid Transceiver” / unsupported optics warning within moments of installation. The same fiber patch and remote device worked normally when left unchanged, but the issue continued whenever that third-party module was used, pointing to a transceiver identification/compatibility problem rather than a cabling or far-end link fault.
How to handle this:
When you see errors like “Invalid Transceiver” or “unsupported optics,” the first step is to make transceiver detection reliable—so the switch can consistently read the module’s Vendor/EEPROM/DDM information and the SFP port isn’t blocked by a recognition issue. GLGNET’s SFP cages and SFP connectors are designed around industry-standard compliance and can be matched to specific platforms and module requirements, helping reduce compatibility risk upfront and improving first-time link bring-up.

Even after compatibility is in place, intermittent “not detected” messages or link flapping often trace back to the physical interface at the port. Tolerance stack-up, contact stability, and front-panel noise can affect the management bus and the electrical bond at the SFP cage interface. GLGNET supports production-friendly mechanical and mounting options (including press-fit variants) and offers EMI gaskets / spring fingers to strengthen shielding and grounding continuity around the panel cutout—helping reduce false alarms and intermittent behavior.
For high-density SFP ports or higher-power modules, it also pays to plan thermal control and service visibility as part of the same front-panel design. GLGNET provides configurable options such as heatsinks (for a more controlled heat path) and light pipes (to bring clear link/activity/fault indication to the faceplate), and supports single-, multiport, and stacked layouts without compromising maintainability—so reliability and field service efficiency scale together.
|
Potential Cause |
Device Behavior |
Recommended Action |
|
Vendor lockout |
Port stays down, error in logs |
Use approved/certified module |
|
Generic module |
Link not established |
Replace with compatible alternative |
|
Unrecognized module |
Device may ignore the SFP |
Verify with vendor specs |
Though it seems basic, an improperly inserted SFP module is a common problem—especially in large switch racks where modules are frequently swapped.
Case example:
A team in the UK troubleshooting a MikroTik CRS328 ran into one SFP port that didn’t respond normally after a module was inserted. The interface stayed down, and the switch would not reliably detect the transceiver in that slot—even though the rest of the switch was operating normally and other ports using the same module type worked as expected. From the outside the module looked “in,” but the port never reached a steady recognized state, indicating a typical “not detected” condition—often seen when the transceiver isn’t fully seated in the SFP cage or the contact isn’t being made consistently.
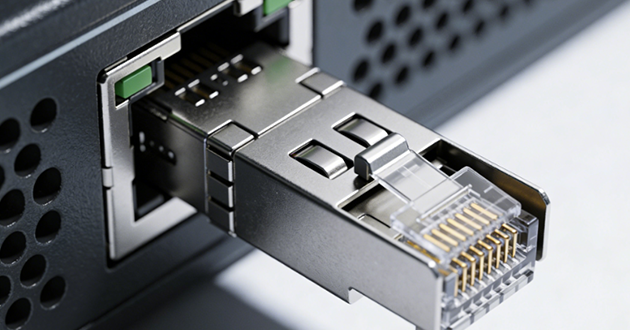
Best practices:
When a module appears to be inserted but the switch still won’t detect it, the issue usually comes down to three things: it isn’t fully seated, the electrical contact isn’t consistent, or the front-panel layout makes installation and checks harder than they should be. These are all problems you can reduce with the right SFP port hardware decisions.
Start with seating and retention. A lot of “not detected” cases happen when the transceiver hasn’t actually latched, even though it looks fine from the outside. An SFP cage + SFP connector design with clear alignment features and a more obvious “fully engaged” feel helps prevent angled insertion and improves mating consistency. GLGNET can match SFP cages and connectors to your faceplate style and port layout, so those mechanical details fit the real chassis instead of relying on best-case assembly.
Next, focus on repeatable contact—especially in dense systems. Small shifts in contact force, mounting approach, or assembly alignment can turn detection into an intermittent problem. Using production-friendly structures (and press-fit options where appropriate) helps keep unit-to-unit variation under control. For tight port banks, light pipe options also make front-panel checks faster by bringing clear per-port status to the faceplate. GLGNET supports multiport and stacked configurations with configurable options, helping balance reliable mating with easier maintenance.
Quick Reminders:
Even if the SFP fits and is compatible, it might be damaged due to poor handling, ESD, or factory defects.
Community report:
A Reddit user in Australia reported that a brand-new SFP transceiver module would not come up on any SFP port they tested. The module wasn’t detected and the link never established, even after trying it in multiple devices and swapping in known-good cables and ports. Another module from the same batch worked normally in the same setups, while the original continued to fail across every test.

How to handle this:
When a brand-new module fails across multiple devices while another unit from the same batch works, don’t keep second-guessing the switch or cabling—treat it as a likely single-unit defect or batch variation. Quarantine the suspect unit, record the lot and serial, and run a quick, repeatable check under identical conditions (same device, same SFP port, same cable, same far end). That keeps the finding traceable and prevents the issue from bouncing between the lab, warehouse, and field.
For a longer-term fix, push risk upstream with a clear Incoming QC plan—sampling or 100% screening depending on the program—focused on catching early failures through targeted electrical and environmental checks. GLGNET supports this with in-house R&D and test capabilities, plus a quality-system approach aimed at delivering consistent, verifiable performance at scale.
At the design level, reduce uncertainty by treating the front-panel interface as a system. Match the SFP cage / SFP connector to your port density, airflow, and power budget, and add thermal or visibility options where they matter. With single-, multiport, and stacked configurations plus customization support, GLGNET helps build a more stable, repeatable SFP port interface—so deployments stay predictable even when component variation is unavoidable.
|
Symptom |
Likely Cause |
Suggested Solution |
|
No link, no LED |
Damaged internal components |
Replace module |
|
Unstable signal |
Intermittent internal fault |
Use a different brand or batch |
|
Cross-device failure |
Manufacturing defect |
Contact supplier or warranty |
SFP ports using fiber modules are vulnerable to connection issues caused by dirt, scratches, or incompatible fiber types.
Real-world incident:
A German ISP saw repeated link drops that happened mostly in the daytime, while the same circuit was much steadier at night. The behavior tracked closely with temperature: as outdoor conditions warmed up, the optical link would lose signal and then come back on its own. Checks then narrowed to the outdoor fiber path and patch points, where several SFP LC connectors showed fine cracking and signs of wear.
As the SFP connectors heated, the damaged housings could flex slightly and the ferrule alignment would shift just enough to raise insertion loss—especially when sunlight warmed the enclosure and cable tension changed—leading to intermittent drops. Overall, the symptoms pointed to a heat-sensitive physical-layer issue caused by compromised outdoor LC terminations.
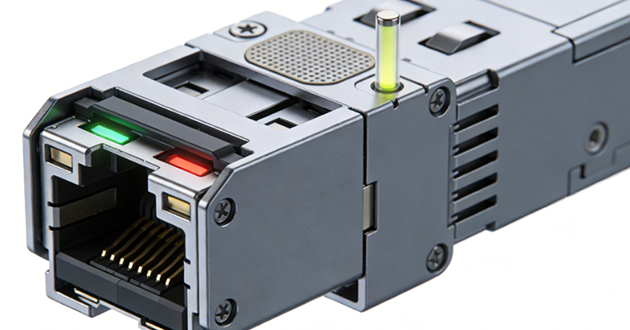
How to handle this:
For temperature-related symptoms like “drops in the daytime, stable at night,” the best approach is to treat the outdoor fiber run as the primary risk area, while also making the equipment-side port interface more robust so the link is less sensitive to environmental changes.
Start with focused outdoor inspection and replacement. Check SFP LC connector patch cords and connection points section by section, and replace anything showing aging, fine cracks, looseness, excessive tension, or bend-radius issues. Confirm splice closures and distribution boxes are properly sealed and include strain relief, so heat expansion, wind, or cable movement can’t introduce subtle shifts. In high-sun locations, adjust routing and add shielding where needed to reduce thermal shock.
In parallel, reinforce the port-side interface. A mechanically stable, well-bonded SFP cage / SFP connector helps keep contact and electrical behavior consistent at the front panel. GLGNET supports multiple SFP port formats and configurable options—such as EMI features, thermal add-ons, and front-panel visibility—so reliability can be designed in more repeatably and overall link stability improves.
Match the module to the fiber type:
|
Issue |
Cause |
Fix |
|
No link light |
Dirty or mismatched fiber |
Clean connectors, confirm fiber type |
|
Fluctuating connection |
Fiber damage or misalignment |
Inspect and replace cable if needed |
|
Partial signal |
Distance exceeds module range |
Use long-range modules (e.g., LX or LR) |
SFP modules on each end of a fiber link must match in type, speed, and wavelength. Mixing different modules, such as LX and SX, will result in no communication.
Enterprise experience:
An IT engineer in the U.S. was troubleshooting a building-to-building fiber link that wouldn’t come up reliably. The core issue was a transceiver mismatch: one end used 1000BASE-SX (multimode) while the other used 1000BASE-LX (single-mode), so the optics didn’t match and the link stayed unstable.

How to handle this:
The fix is simple: treat the fiber link as a paired system and make sure both ends use the same optical spec—same speed, the same fiber type/wavelength (MMF vs. SMF), the same interface, and a reasonable power budget match. In practice, pick the optic based on the installed fiber and distance (short multimode runs → standardize on SX; single-mode or longer runs → standardize on LX), and swap the transceivers as a matched pair so one end isn’t unknowingly running a different optical type.
To keep it from happening again, make transceiver selection repeatable and documented. Capture the optic type, fiber type, distance range, and acceptance checks in the BOM or deployment checklist, and add a quick end-to-end “pair check” before commissioning or handover. On the hardware side, standardizing on a consistent, broadly compatible SFP cage / SFP connector platform across your equipment helps reduce variation during rollouts. GLGNET provides multiple cage and connector formats—single, multiport, and stacked—with customization support, making it easier to keep the SFP port interface consistent across platforms and reduce mismatches in the field.
Sometimes the SFP hardware works fine, but a simple software misconfiguration prevents it from functioning.
Consultant case:
A network engineer in New York couldn’t get a Cisco Catalyst 2960X SFP port to come up, even though the module was installed. The core issue turned out to be simple: the interface was administratively disabled (shutdown), so the SFP port stayed down until it was enabled.

How to handle this:
If the transceiver is in place but the SFP port won’t come up, the fastest win is to rule out a simple config state: the interface may still be shut down. Make sure it’s enabled, then do a quick check of the usual blockers—port mode, speed/auto-negotiation expectations, and VLAN/trunk settings. Also confirm the port isn’t being forced down by a protection mechanism (such as a security policy or an error-disabled state), so you don’t chase hardware when it’s really configuration.
After the software side is confirmed, look at the port hardware to avoid avoidable deployment “gotchas.” A robust, widely compatible SFP cage / SFP connector setup helps reduce problems caused by borderline insertion, inconsistent contact, or a sensitive front-panel interface. GLGNET provides SFP cages and connectors in single-, multiport-, and stacked formats, with options like EMI, thermal, and front-panel indicator features—supporting more consistent, service-friendly SFP port implementations across different platforms.
|
Setting |
Possible Problem |
Fix |
|
Port shutdown |
Port not active |
Run “no shutdown” |
|
VLAN mismatch |
No connectivity |
Reassign correct VLAN |
|
Speed/duplex mismatch |
Link flaps or no link |
Enable auto-negotiation or set correct speed manually |
Read more:
https://www.glgnet.biz/articledetail/what-does-sfp-stand-for.html
Conclusion:
Most SFP port failures can be traced to a few common causes: incompatible modules, faulty cables, mismatched wavelengths, or configuration errors.
By following the steps in this guide, you can quickly identify and fix SFP port issues—whether you're supporting an enterprise switch or a small business router.
Still facing issues with your SFP ports? Don’t hesitate to contact GLGNET or reach out to a qualified networking professional for further support.